apply & call & bind 异同
🎯 核心异同对比表
| 方法 | 执行时机 | 参数形式 | 返回值 | 典型场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| call | 立即执行 | 参数列表 | 无 | 明确参数个数时调用 |
| apply | 立即执行 | 数组 | 无 | 参数个数不确定/数组参数展开时使用 |
| bind | 延迟执行 | 参数列表(可分批传递) | 绑定后的函数 | 需要保留 this 上下文(如事件回调)时使用 |
1️⃣ 共同目标
三者均用于 显式绑定函数执行时的 this 上下文,解决 this 指向不确定性问题。
2️⃣ 核心差异
📌 参数形式
call(thisArg, arg1, arg2...)参数逐个传递,适合明确参数数量的场景:
javascript
function greet(time, message) {
console.log(`${time}, ${this.name}! ${message}`);
}
greet.call({ name: '灵码' }, '上午好', '今天天气不错'); // ✅ 上午好, 灵码! 今天天气不错apply(thisArg, [argsArray])参数以数组形式传递,适合动态参数或数组展开:
javascript
const numbers = [3, 1, 4];
Math.max.apply(null, numbers); // ✅ 4(等同于 Math.max(3,1,4))bind(thisArg, arg1, arg2...)参数可分批传递,返回绑定后的函数:
javascript
const boundGreet = greet.bind({ name: 'Lingma' }, '晚上好');
boundGreet('该休息了'); // ✅ 晚上好, Lingma! 该休息了📌 执行时机
call/apply:立即执行函数
javascript
function log() { console.log(this.id); }
log.call({ id: 100 }); // ✅ 立即输出 100bind:返回新函数,需手动调用:
javascript
const boundLog = log.bind({ id: 200 });
boundLog(); // ✅ 手动调用后输出 2003️⃣ 特殊场景示例
🌰 组合使用 bind 与 call
javascript
function multiply(a, b) {
return a * b * this.factor;
}
const boundFn = multiply.bind({ factor: 2 }, 3); // 绑定 this 和第一个参数
boundFn.call({ factor: 5 }, 4); // ❗️ 输出 24(3 * 4 * 2),bind 的 this 优先级更高🌰 事件监听中的 bind
javascript
class Button {
constructor() {
this.text = '点击';
this.element.addEventListener('click', this.handleClick.bind(this)); // 绑定 this
}
handleClick() {
console.log(this.text); // ✅ 正确指向 Button 实例
}
}⚠️ 注意事项
非函数调用会报错:
javascript
({}.bind)(); // ❌ TypeError: {}.bind is not a function严格模式下的 this:
若首个参数为 null[/](file://f:\A-Source\Vue2\vue\BACKERS.md)undefined,严格模式下 this 指向 undefined,非严格模式指向全局对象。
🛠️ 总结
- 共同点:控制函数 this 指向。
- 差异点:
- call:参数列表 + 立即执行
- apply:数组参数 + 立即执行
- bind:参数分批 + 延迟执行
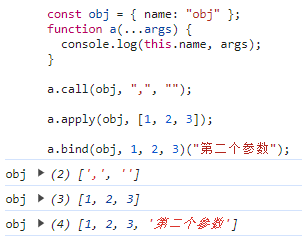
js
const obj = { name: "obj" };
function a(...args) {
console.log(this.name, args);
}
a.call(obj, ",", "");
a.apply(obj, [1, 2, 3]);
a.bind(obj, 1, 2, 3)("第二个参数");